At its heart, cryptocurrency is simply digital money. It's a way for you to send value directly to another person, completely cutting out the middleman like a bank or credit card company. Think of it like a digital version of cash, but instead of being protected by a bank vault, it's secured by powerful encryption. This core concept is the launchpad for the entire world of crypto.
In This Guide
- 1 What Is Cryptocurrency in Simple Terms
- 2 The Journey from Digital Cash to Global Asset
- 3 Understanding the Different Kinds of Crypto
- 4 How to Buy Your First Cryptocurrency Securely
- 5 Choosing and Mastering Your Crypto Wallet
- 6 Navigating the Risks and Common Pitfalls of Crypto
- 7 Got Questions? Here Are the Top 10 Things Newcomers Ask
- 7.1 1. How much money do I need to start investing in cryptocurrency?
- 7.2 2. Is cryptocurrency anonymous?
- 7.3 3. What happens if I lose my private keys or seed phrase?
- 7.4 4. Do I have to pay taxes on my cryptocurrency?
- 7.5 5. What's the difference between a coin and a token?
- 7.6 6. Can I reverse a cryptocurrency transaction?
- 7.7 7. Why is cryptocurrency so volatile?
- 7.8 8. Is it too late to invest in Bitcoin?
- 7.9 9. Which crypto is the best one for beginners to buy?
- 7.10 10. What does "decentralization" actually mean in practice?
What Is Cryptocurrency in Simple Terms

To really get a handle on how cryptocurrency works, let's use a simple analogy. Imagine a shared digital notebook that everyone in a network can see and access. This shared notebook is what we call the blockchain.
Every time a transaction happens—say, "Alex pays Ben 1 Bitcoin"—a new line is added to the notebook. Once a page is filled with these transaction records, it's sealed shut with a unique cryptographic lock and added to the end of the chain, creating a permanent, unchangeable record.
This "shared notebook" idea is what makes crypto so different from traditional finance. It has a few game-changing features:
- Transparency: Since everyone on the network has a copy of this notebook, all transactions are out in the open. Anyone can look at the ledger and verify them.
- Immutability: Once a page of transactions is locked and added to the chain, it's practically set in stone. To change it, you'd have to alter that page on thousands of computers all at once, which is next to impossible. This makes the system incredibly secure.
- Decentralization: No single person, company, or government owns the notebook. It's maintained by a vast, global network of computers, meaning no one can unilaterally change the rules or block a legitimate transaction.
This structure is what allows people to interact and transact directly with each other, without needing a trusted third party like a bank to sign off on everything.
Security Without a Middleman
So, if there's no central authority, what keeps everything secure? The system's integrity relies on cryptography—the science of secure communication using complex math.
When you want to send crypto, you authorize the transaction with a unique digital signature known as a private key. You can think of this as your secret password or the physical signature you'd use on a check. It’s the one thing that proves you're the true owner of the funds and have the right to send them.
Key Takeaway: The blockchain is a secure, transparent public ledger for all transactions. Cryptography ensures that only the rightful owner can access and manage their funds, making traditional financial go-betweens unnecessary.
This decentralized framework is the foundational innovation that started with Bitcoin and has since powered thousands of other cryptocurrencies. To dig even deeper, check out our full guide on what is cryptocurrency and how does it work right here on our site.
Ultimately, this technology offers a new way to transfer value over the internet that is open, globally accessible, and resistant to censorship. It’s more than just a new form of money; it's an entirely new blueprint for financial systems.
The Journey from Digital Cash to Global Asset
The idea of a purely digital form of cash isn't new. For decades, computer scientists and cryptographers tried to crack the code, but one major hurdle always stood in their way: the double-spending problem.
Simply put, how do you prevent someone from spending the same digital coin multiple times? Without a central authority like a bank to validate every transaction, it seemed like an impossible puzzle to solve.
That all changed in 2009. An anonymous person or group known only as Satoshi Nakamoto published the now-famous Bitcoin whitepaper. It wasn't just another theory; it was a practical, elegant solution that wove together existing cryptographic ideas in a completely novel way.
Nakamoto’s genius was in using the blockchain—that distributed public ledger we covered earlier—to solve the double-spending issue once and for all. This created a system where a network of users, not a bank, confirmed and recorded every transaction, making digital counterfeiting practically impossible.
The Rise of Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s timing was no accident. Arriving on the heels of the 2008 financial crisis, it offered a radical alternative to a traditional system that many felt had failed them. It was a vision for finance where you, the individual, held all the power.
Its purpose was clear and revolutionary:
- Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Let anyone send money directly to anyone else, anywhere in the world, without an intermediary.
- Censorship Resistance: Make it impossible for a government or corporation to freeze your funds or block a legitimate transaction.
- Provable Scarcity: Cap the total supply at 21 million coins forever, hardcoding a defense against inflation.
This design carved out a new asset class entirely—one that was global, permissionless, and not under any single entity's control.
Ethereum Unlocks New Possibilities
For its first few years, crypto was pretty much just Bitcoin. But in 2015, a new platform called Ethereum showed up and completely changed the conversation. Ethereum’s founders looked at blockchain technology and asked, "What if it could do more than just track money?"
They made the blockchain programmable by introducing smart contracts. These are just like regular contracts, but they are written in code and automatically execute themselves when the conditions are met.
Real-Life Example: Imagine you're booking an Airbnb. A smart contract could hold your payment in escrow. The moment the host's smart lock registers your check-in, the contract automatically releases the funds to them. No intermediaries, no payment delays—just code executing a pre-agreed deal.
This single innovation threw the doors wide open. Suddenly, developers could build all sorts of applications on top of a blockchain, from decentralized lending platforms to digital art marketplaces.
As this technology continues to develop, the market is expected to grow alongside it. Some analysts project the global cryptocurrency market could expand from USD 5.7 billion to over USD 11.7 billion by 2030.
This is also where specific projects and their potential come into focus. The Ethereum network, for example, has drawn massive attention from institutional investors, a trend you can explore further in our piece on the Ethereum bet billionaires are backing. This evolution—from a simple idea for digital money to a programmable platform for a new kind of internet—is why cryptocurrency is so much more than just a passing trend.
Understanding the Different Kinds of Crypto
Diving into crypto for the first time can feel a bit overwhelming. You're met with thousands of different coins, and it’s not always clear what separates one from the next. The good news is that most of them fall into a few main categories, each with its own purpose and personality.
Getting a handle on these categories is the first real step toward navigating the crypto world with confidence. Let's start with the two you'll hear about most often: Bitcoin and Ethereum. People tend to lump them together, but they were built for fundamentally different jobs.
Bitcoin: The Original Digital Gold
Bitcoin (BTC) was the one that started it all. Its original goal was to create a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that didn't need banks. Over the years, however, its role has shifted.
Because there will only ever be 21 million coins created, Bitcoin has become known as a store of value—think of it like digital gold. Its main job today is to provide a secure, decentralized way to hold and transfer value, completely separate from the traditional financial system. It’s simple, powerful, and has the longest track record in the game.
Ethereum: The World Computer
Ethereum (ETH) came along later with a much broader ambition. It’s not just digital money; it’s a programmable blockchain that lets developers build and run decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts right on top of it.
Here’s a good way to think about it: if Bitcoin is a calculator that’s really good at one thing (math), Ethereum is a smartphone. You can still use it as a calculator, but its real power comes from the thousands of apps you can run on it for everything from finance and gaming to creating digital art.
The image below gives a great snapshot of the economic scale of these two giants.
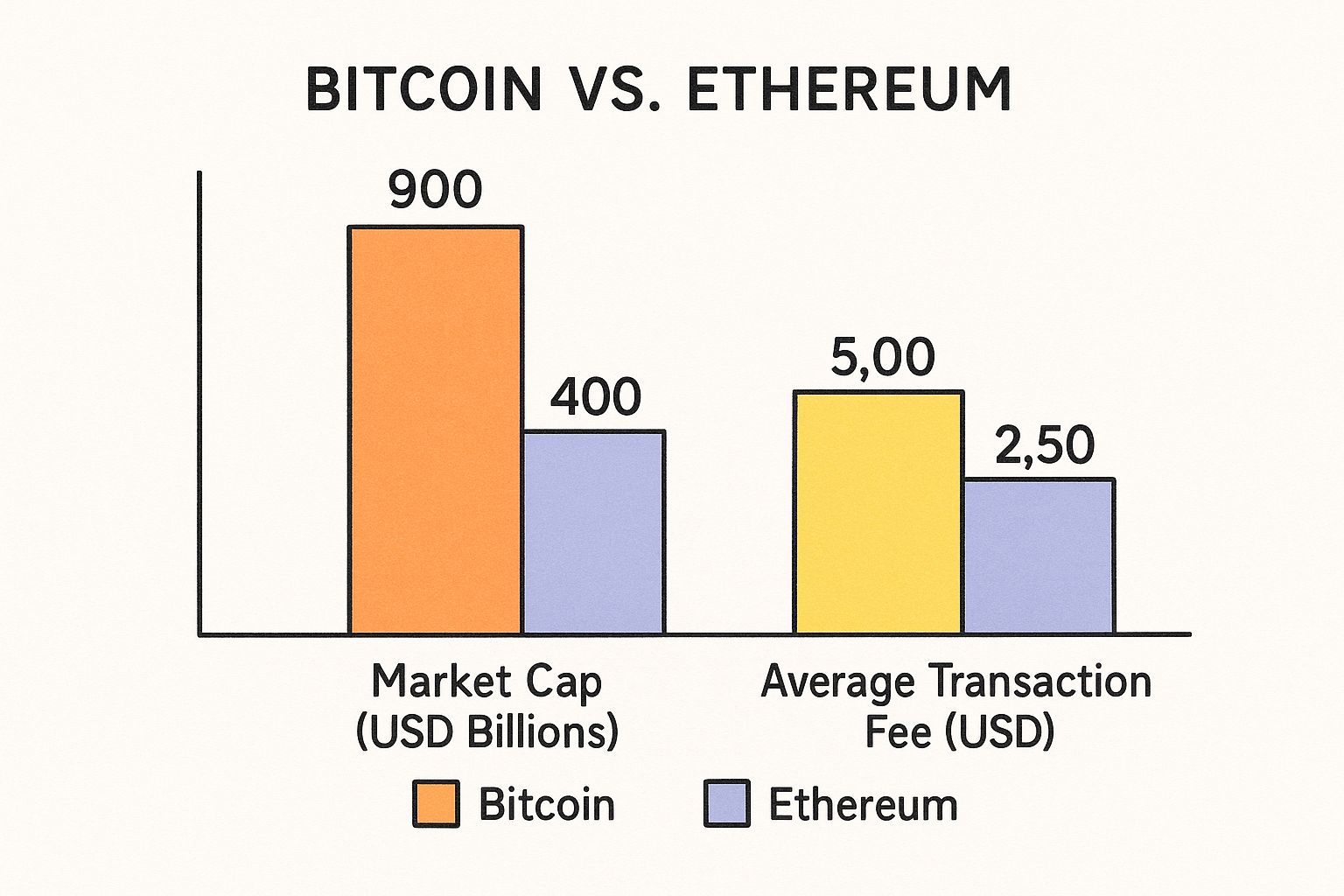
You can see that while Bitcoin boasts a larger overall market cap, Ethereum’s network often has higher transaction fees. This reflects the constant demand for its processing power to run all those dApps.
Altcoins, Stablecoins, and Meme Coins
Once you move past the big two, a whole universe of other crypto assets opens up. They generally fall into one of these buckets:
- Altcoins: This is basically a catch-all term for any crypto that isn't Bitcoin. Some are direct competitors to Bitcoin or Ethereum, while others are designed for highly specific jobs, like enhancing privacy or tracking supply chains.
- Stablecoins: These are a special class of crypto built for one thing: stability. They hold their value by being "pegged" to a real-world asset, usually the U.S. dollar. For example, USD Coin (USDC) is designed to always be worth $1.
- Meme Coins: These coins, like the famous Dogecoin, often start as an internet joke. Their value isn't based on technology or a real-world use case; instead, it's driven almost entirely by community hype and social media trends, which makes them incredibly unpredictable and risky.
Comparing Major Cryptocurrency Categories
This table breaks down the core purpose, a key example, and the typical risk level for different types of cryptocurrencies.
| Crypto Type | Primary Purpose | Key Example | Typical Volatility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Store of Value | To act as a decentralized form of digital gold, preserving wealth over time. | Bitcoin (BTC) | High |
| Smart Contract Platform | To provide the infrastructure for building decentralized applications. | Ethereum (ETH) | High |
| Stablecoin | To maintain a stable price pegged to a fiat currency like the U.S. dollar. | USD Coin (USDC) | Very Low |
| Meme Coin | To build a community-driven asset, often fueled by hype and social trends. | Dogecoin (DOGE) | Extremely High |
Understanding this basic framework is a game-changer. It helps you look past the hype and start to see where a particular coin might fit into the bigger picture—and more importantly, whether it fits into your own financial goals.
The type of crypto you choose to explore really comes down to your personal goals and how much risk you're comfortable with. If you're looking for a deeper dive into evaluating specific projects, our guide on what is the best cryptocurrency to invest in right now is a great next step.
How to Buy Your First Cryptocurrency Securely
Alright, let's talk about the exciting part: making your first crypto purchase. Getting this right from the start is all about security. Your main entry point into the crypto world will be a cryptocurrency exchange—basically a digital marketplace where you can buy, sell, and trade assets. Think of it as a stock brokerage, but for the digital age.
The very first choice you have to make is picking the right exchange. For anyone new to this, the best platforms are the ones that don't overcomplicate things. You want an exchange that’s easy to use, has rock-solid security, and doesn't hide its fees in the fine print. These platforms act as the bridge from your regular bank account into the crypto ecosystem.
Step 1: Choose a Reputable Exchange
Let me be clear: not all crypto exchanges are created equal. Some are built for Wall Street-style traders, with dizzying charts and complex order books. Others are designed from the ground up for beginners. As someone just starting out, stick with platforms known for being user-friendly and obsessed with security.
You'll generally find two types of exchanges: those built for simplicity and those packed with features for advanced users. Here’s a quick breakdown to help you see the difference.
| Feature | Beginner-Friendly Exchange (e.g., Coinbase) | Advanced Exchange (e.g., Binance) |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | Simple and clean. Made for people buying for the first time. | More complex, with advanced charts and trading tools. |
| Asset Selection | A curated list of the big, well-known cryptocurrencies. | A massive menu of assets, including many smaller, riskier altcoins. |
| Security | Top-tier security, often with insurance for your cash deposits. | Strong security, but you're expected to know more to stay safe. |
| Fees | Usually a bit higher to pay for the simple, convenient experience. | Lower fees, especially if you trade in large volumes. |
For your first purchase, I almost always recommend a beginner-focused exchange. It cuts out the noise and lets you focus on the fundamentals: buying your crypto and keeping it safe.
Step 2: Set Up and Verify Your Account
Once you've picked an exchange, it's time to create your account. This part is pretty straightforward, but pay close attention to the security details—they matter more than anything else.
- Sign Up: You’ll start with the basics: name, email, and a password. Please, create a strong, unique password for this. Don't recycle one you use elsewhere.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This is absolutely non-negotiable. 2FA adds a powerful second layer of defense. It requires a code from your phone (ideally from an app like Google Authenticator) whenever you log in. This one step makes it incredibly difficult for someone to get into your account, even if they steal your password.
- Complete Identity Verification (KYC): Legitimate exchanges are required by law to verify who you are. This is called Know Your Customer (KYC). You'll likely need to upload a photo of a government ID (like a driver's license) and maybe snap a selfie.
Don't be put off by this verification step. It's actually a good sign. It means the platform is regulated and working to prevent fraud, which is what you want.
Step 3: Fund Your Account and Make Your Purchase
With your account set up and secured, you're ready to buy. First, you need to get money onto the exchange. Most platforms give you a few options, like a bank transfer (ACH), wire transfer, or a debit card. Just a heads-up: debit card purchases are usually instant, but they often come with slightly higher fees.
Once your account is funded, you can place your first order. The simplest way to do this is with a market order. This just means you're telling the exchange, "I want to buy crypto at its current price." You simply type in how much money you want to spend, click "buy," and the exchange handles the rest.
This entire process is becoming more and more common. Recent data shows cryptocurrency ownership has climbed from 21% to nearly 24% in key global markets, thanks in part to clearer rules and wider acceptance. You can dig into the numbers in the full 2025 Global State of Crypto report from Gemini.
For a deeper dive into building a strategy, be sure to read our guide on how to invest in cryptocurrency. And just like that—congratulations, you're now a crypto owner.
Choosing and Mastering Your Crypto Wallet
So, you’ve bought some crypto on an exchange. Now comes the most important decision you'll make: where to store it. You could just leave it on the exchange, but that comes with risks. In the crypto world, you'll hear one phrase repeated like a mantra: “Not your keys, not your coins.”
This saying gets right to the heart of what it means to truly own your digital assets. When your crypto sits on an exchange, you're trusting them to hold your private keys for you. In effect, they have custody of your money. A crypto wallet, on the other hand, puts you in direct control of those keys. It’s the difference between leaving your cash in a bank versus keeping it in a personal safe at home. You are your own bank.
Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets
Crypto wallets generally come in two main flavors: hot and cold. Each serves a different purpose, and understanding the distinction is your first step toward building a solid security setup.
A hot wallet is any wallet connected to the internet. Think mobile apps, desktop software, or browser extensions. Their constant online connection makes them incredibly convenient for everyday use—sending, receiving, and trading crypto is quick and easy. But that same connectivity makes them inherently more vulnerable to online threats like hacking and malware.
A cold wallet, often called a hardware wallet, is a physical device that keeps your private keys completely offline. These gadgets, which usually look like a USB stick, only connect to the internet for the brief moment you need to sign and approve a transaction. This "air-gapped" approach makes them the gold standard for security and the go-to choice for storing significant amounts of crypto for the long haul.
Choosing the Right Wallet for You
The best way to think about this is with a real-world parallel. A hot wallet is like the cash you carry in your pocket or the money in your checking account—it’s for easy access and daily spending. A cold wallet is like your savings account or the safe in your closet—it’s where you store the bulk of your wealth securely.
This table breaks down the key differences between the two.
| Feature | Hot Wallet (Software) | Cold Wallet (Hardware) |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Always online | Mostly offline |
| Best For | Frequent, small transactions and daily use. | Long-term holding (HODLing) and large amounts. |
| Convenience | High. Access funds instantly from your phone or computer. | Lower. Requires the physical device to access funds. |
| Security | Good, but vulnerable to online attacks. | Excellent. Protected from online threats. |
| Examples | MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Exodus | Ledger, Trezor |
For most people, especially beginners, a hybrid approach works best. Keep a small, usable amount of crypto in a reputable hot wallet for convenience, and transfer the rest of your holdings to a secure cold wallet for safekeeping.
Securing Your Seed Phrase
No matter which type of wallet you choose, you'll be given a seed phrase (also called a recovery phrase) during the setup process. This is typically a list of 12 or 24 random words that acts as the master backup for your wallet.
CRITICAL: Your seed phrase is the ultimate key to all your cryptocurrency. Anyone who gets their hands on this phrase can access and drain your wallet. You must protect it above all else.
Here's exactly how to handle it:
- Write It Down: Use a physical pen and paper. Never, ever store it as a digital text file, a screenshot, or a photo on your phone or computer.
- Store It Securely: Hide your written phrase somewhere safe, private, and secure. Some people even make multiple copies and store them in different physical locations.
- Never Share It: No legitimate company, developer, or support agent will ever ask you for your seed phrase. Anyone asking for it is a scammer, 100% of the time.
Learning to properly manage a wallet and protect your seed phrase are the most vital skills you'll develop on your crypto journey. This is the step that takes you from being a passive owner to a sovereign individual in full control of your own assets.
Alright, let's have an honest conversation about the risks. To succeed in crypto, you have to understand the challenges, and this world definitely has its fair share of them. Think of this section as your map through the sometimes wild and tricky terrain of the crypto market. Knowing the dangers is the first step to keeping your money safe.
The first thing you'll notice about crypto is its volatility. Prices can swing wildly in a single day—sometimes in a matter of hours. It’s totally normal to see a major coin jump or drop 10% (or more) because of a single news story, a government announcement, or just a change in how the market feels that day.
This is a classic double-edged sword. Sure, it’s how people make incredible gains, but it also means beginners can face huge, fast losses if they aren't ready for the ride.
Riding the Waves of Market Volatility
Unlike the stock market with its opening and closing bells, the crypto market never sleeps—it’s open 24/7. This means prices are always on the move. For a real-world gut check, look at the crash in May 2021. Bitcoin’s price plunged by over 30% in just one day.
Key Takeaway: Never, ever invest more than you can comfortably afford to lose. This isn't just a friendly tip; it's the golden rule of crypto. The market's insane swings can be an emotional rollercoaster, so having a solid strategy is non-negotiable.
A good plan helps you stay level-headed when prices go haywire. If you want to build a more robust approach, our guide to cryptocurrency investment strategies is a great place to learn about thinking long-term.
How to Spot and Dodge Common Scams
Unfortunately, all the excitement in crypto acts like a magnet for scammers. Newcomers are their favorite targets because they're still learning the basics. Your best defense is simply knowing what their tricks look like.
Keep an eye out for these classic red flags:
- Phishing Scams: You get an email or a direct message that looks like it's from your exchange or wallet provider. It will create a sense of urgency, asking you to "verify your account" by clicking a link. That link leads to a convincing but fake website designed to steal your login info or seed phrase.
- "Too Good to Be True" Promises: If a project or person promises you guaranteed, sky-high returns with zero risk, run. Every real investment has risk, and anyone who tells you otherwise is trying to pull a fast one.
- Celebrity Impersonator Giveaways: This one is rampant on social media. Scammers create fake profiles of famous people like Elon Musk and promise to double any crypto you send them. The reality? Any crypto you send is gone for good.
Dodging the Psychological Traps
Sometimes the biggest risks aren't from scammers, but from our own brains. Human psychology can lead to some really bad financial moves, especially in a market that runs on pure emotion.
Two of the biggest mental traps for beginners are FOMO and panic selling.
| Psychological Trap | What It Feels Like | How to Beat It |
|---|---|---|
| FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out) | You see a coin's price rocketing up and feel a powerful urge to buy in at the top. You're terrified you'll miss out on even more gains. | Trust the plan you made when you were calm and rational. Don't make impulsive trades based on hype. |
| Panic Selling | The market takes a nosedive, and fear kicks in. You rush to sell everything at a loss just to stop the bleeding. | Remember why you invested in the first place. Volatility is part of the game; selling in a panic just turns a paper loss into a real one. |
Ultimately, the goal is to enter this market with a healthy dose of skepticism and a clear head. By understanding the volatility, knowing how to spot a scam, and keeping your own emotions in check, you can protect your investment and make smarter choices on your crypto journey.
Got Questions? Here Are the Top 10 Things Newcomers Ask
We've covered a lot of ground, from blockchains to wallets. To tie it all together, let's walk through some of the most common questions that come up when you're just getting started. Think of this as your quick-reference guide for those lingering "what ifs."
1. How much money do I need to start investing in cryptocurrency?
You don't need a fortune. Most major exchanges allow you to buy fractions of a cryptocurrency, meaning you can start with as little as $10 or $20. The most important rule is to only invest an amount you are fully prepared to lose, especially when you are just beginning.
2. Is cryptocurrency anonymous?
No, it is pseudonymous. This means that while your real name isn't attached to your transactions, every transaction is permanently recorded on the public blockchain. Your wallet address is visible, and with enough analysis, transactions can sometimes be traced back to an individual.
3. What happens if I lose my private keys or seed phrase?
If you lose your seed phrase and cannot access your wallet, your funds are likely lost forever. There is no central authority or customer service to help you recover them. This is why it is absolutely critical to write down your seed phrase and store it in a secure, offline location.
4. Do I have to pay taxes on my cryptocurrency?
In most countries, including the United States, yes. Cryptocurrencies are typically treated as property for tax purposes. This means you may owe capital gains tax when you sell, trade, or even use your crypto to buy goods or services if its value has increased since you acquired it. Tax regulations can be complex, so consulting with a tax professional is highly recommended.
5. What's the difference between a coin and a token?
A coin (like Bitcoin or Ethereum) operates on its own independent blockchain. A token, on the other hand, is built on top of an existing blockchain platform, like Ethereum's ERC-20 standard. Think of the blockchain as an operating system (like iOS) and tokens as the apps that run on it.
6. Can I reverse a cryptocurrency transaction?
No. Once a transaction is confirmed on the blockchain, it is permanent and irreversible. This is a core feature of the technology. Always double-check the recipient's address before sending funds, as sending to the wrong address means the funds are gone for good.
7. Why is cryptocurrency so volatile?
Crypto's value is driven by supply and demand, but the market is still relatively new and speculative. Factors like regulatory news, technological developments, social media hype (especially for meme coins), and macroeconomic trends can cause rapid and significant price swings.
8. Is it too late to invest in Bitcoin?
This is a common question without a simple answer. While the days of buying Bitcoin for a few dollars are long gone, many investors still see it as a long-term store of value, akin to "digital gold," with potential for future growth. Others believe its biggest gains are in the past. It remains a high-risk asset, and any investment decision should be based on thorough research and your personal financial situation.
9. Which crypto is the best one for beginners to buy?
For beginners, Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) are generally considered the most straightforward starting points. They have the longest track record, the largest market capitalizations, and the most resources available for learning. The "best" investment, however, always depends on your individual research, risk tolerance, and investment goals.
10. What does "decentralization" actually mean in practice?
Decentralization means there is no single point of control or failure. Instead of a bank or government managing the network, power is distributed among all the participants (nodes) across the globe. In practice, this means no single entity can censor transactions, freeze your funds, or unilaterally change the rules of the system, making it highly resilient and permissionless.
Ready to continue your wealth-building journey? For more expert insights on stocks, real estate, and crypto, subscribe to Top Wealth Guide and gain access to actionable strategies to secure your financial future. Visit us today at https://topwealthguide.com.
